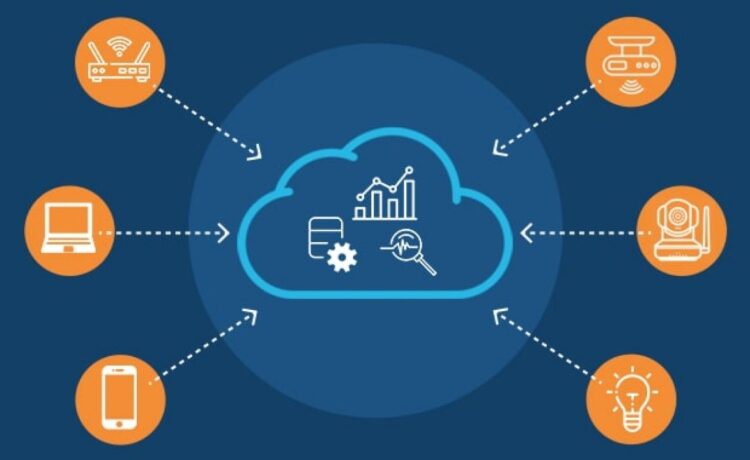
The Internet of Things has revolutionized our interactions with technology, allowing for more efficient and effective solutions in various industries. IoT solutions, such as smart home devices, healthcare monitoring systems, and industrial automation, are becoming increasingly popular as they offer convenience and real-time data analysis. However, an IoT platform is required to manage and analyze this data effectively. In recent years, the cloud-native architecture has emerged as an innovative solution for developing and deploying IoT platforms.
This blog will explain the advantages, obstacles, and adoption strategies for IoT platforms using cloud-native architecture.
Advantages of IoT platforms using cloud-native architecture
● Scalability
The cloud-native architecture allows for easy scalability of IoT platforms. Traditional platforms rely on hardware, making it difficult and expensive to scale up or down. Cloud-native IoT platforms, on the other hand, can easily adjust resources based on demand. This scalability enables businesses to respond quickly to changes in usage patterns and avoid overprovisioning or underprovisioning resources.
● Flexibility
Cloud-native IoT platforms are flexible in their design, enabling customization and integration with other systems. This flexibility means businesses can create tailored solutions that meet their specific needs. Additionally, cloud-native platforms can integrate with third-party services, reducing development time and costs.
● Cost-effectiveness
Cloud-native IoT platforms eliminate the need for expensive hardware and reduce maintenance costs. Instead, businesses pay for what they use, making it more cost-effective. This allows businesses to allocate resources to other areas of their operations.
● Resilience and reliability
Cloud-native IoT platforms are designed for high availability and reliability. They are built with redundancy, ensuring that if one part of the platform fails, there is another to take over. Additionally, cloud-native platforms provide real-time monitoring, allowing for early detection and resolution of issues.
Obstacles to the adoption of cloud-native IoT platforms
Integration challenges
One of the main obstacles to adopting cloud-native IoT platforms is integrating them with existing systems. Migrating from traditional platforms to cloud-native architecture can be complex and requires planning and investment. Additionally, cloud-native platforms may require a different skill set to manage and maintain them.
Security concerns
IoT solutions can present security challenges due to the large amount of data they collect and transmit. Cloud-native IoT platforms are no exception. It is crucial to ensure that security measures are in place to protect against data breaches and cyber-attacks. This requires expertise and investment in security measures.
Skills gap
Adopting cloud-native IoT platforms requires specialized skills that may not be readily available. Businesses must invest in training and development to build the necessary skills to manage and maintain the platform. The skills gap may also result in higher costs for development and management.
Adoption strategies for cloud-native IoT platforms
Plan for integration
To ensure a smooth transition to a cloud-native architecture, businesses should have a clear plan for integration. This includes identifying any potential issues and planning for how to overcome them. Additionally, businesses should prioritize testing and validation to ensure the platform works seamlessly with existing systems.
Prioritize security
Security should be a top priority when adopting cloud-native IoT platforms. Businesses must conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities. Additionally, they should invest in security measures such as data encryption, access control, and monitoring. Regular security audits and updates should also be performed to stay ahead of potential threats.
Invest in training and skill development:
To overcome the skills gap, businesses should invest in training and skill development for their staff. This includes hiring or training IT staff with cloud-native architecture skills and investing in online training and certification programs. By building a skilled workforce, businesses can better manage and maintain the platform and reduce costs associated with outsourcing.
Conclusion
Cloud-native architecture has emerged as a viable solution for developing and deploying IoT platforms. It offers several advantages: scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and resilience. However, adopting cloud-native IoT platforms can present obstacles such as integration challenges, security concerns, and skills gaps. To overcome these obstacles, businesses should plan for integration, prioritize security, and invest in training and skill development. By adopting cloud-native IoT platforms, businesses can take advantage of the benefits offered by IoT solutions and stay competitive in their respective industries.